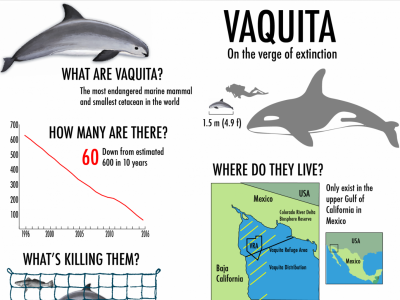
Five key aspects of sustainable aquaculture: Can aquaculture help tackle global food security, especially in Africa?
by Muhammed Oyinlola, Nereus Fellow
Aquaculture, the farming of aquatic species, is gradually becoming an important aspect of solving the challenge of global food security. The supply of seafood from fisheries is declining; fish stocks can only be increased if we reduce our fishing pressures, yet governments continue to subsidize the fishing industry for us to fish more. Hence, the open window we have is aquaculture. My argument is that we need to change from hunting in the ocean to farming the oceans just the way we changed hunting on land to producing animal protein by farming. Can aquaculture be our best option to increase the seafood supply for the world’s ever increasing population?