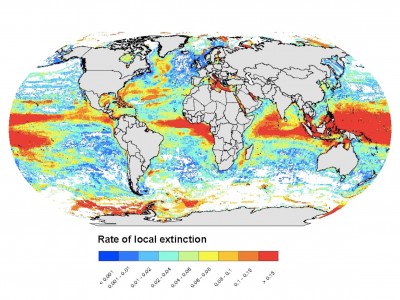
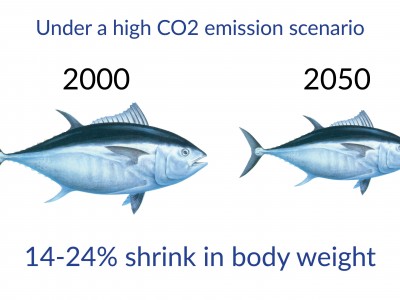
Climate, Anchovy, and Sardine
According to the FAO, anchovy and sardine made up 13% of global catch in 2012. These small fish are consumed by humans, marine mammals, seabirds, squid, and other fish. They are also used for aquaculture feed, industrial oil, and health supplements. “Climate, Anchovy, and Sardine” a new study in the Annual Review of Marine Science, co-authored by Nereus Alumni Rebecca Asch (Princeton University) and Ryan Rykaczewski (University of South Carolina), reviews the past, present, and future of anchovy and sardine.