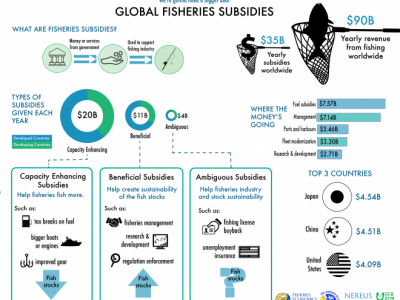
Global seafood trade flows and developing economies: Insights from linking trade and production
Seafood is one of the highest valued food items traded among countries around the world. Seafood exceeds the trade value of sugar, maize, coffee, rice and cocoa combined. But where is this seafood going and who is most benefiting?