West African fisheries, climate change, and aquaculture: A World Bank and Sub Regional Fisheries Commission workshop
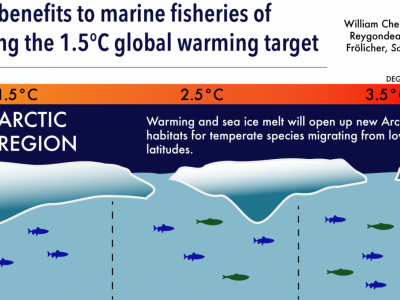
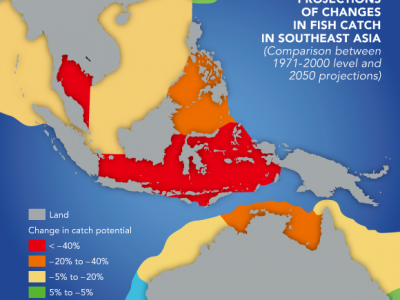
West Africa may be one of the most vulnerable regions to climate change. The region is highly dependent on fisheries for livelihoods and as an important food source. The marine resources of West Africa are currently threatened by overfishing and climate change-induced ocean warming could see fish stocks migrate away from the area and into cooler waters. If CO2 emissions continue at their current levels, the region could see a 50% decline in fisheries-related jobs and a total annual loss of US$311 million, found a study by Nereus Program researchers.