Daniel Pauly, Chair of the Nereus Steering Committee and a member of the Advisory Board, and William Cheung, Director of the Nereus Program (Science) and Principle Investigator, have co-authored a paper titled “Polar lessons learned: long-term management based on shared threats in Arctic and Antarctic environments” (DOWNLOAD PDF) in Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment. This paper looks at the threats to the Arctic and Antarctic polar regions, including climate change, pollution, fisheries overexploitation, and invasive species. The paper advises that “until the greenhouse-gas emissions that drive climate change can be reduced, it is crucial to address other threats (including pollution, fisheries overharvesting, and invasive species) that interact with climate change.”
Abstract:
The Arctic and Antarctic polar regions are subject to multiple environmental threats, arising from both local and ex-situ human activities. We review the major threats to polar ecosystems including the principal stressor, climate change, which interacts with and exacerbates other threats such as pollution, fisheries overexploitation, and the establishment and spread of invasive species. Given the lack of progress in reducing global atmospheric greenhouse-gas emissions, we suggest that managing the threats that interact synergistically with climate change, and that are potentially more tractable, is all the more important in the short to medium term for polar conservation. We show how evidence-based lessons learned from scientific research can be shared between the poles on topics such as contaminant mitigation, biosecurity protocols to reduce species invasions, and the regulation of fisheries and marine environments. Applying these trans-polar lessons in tandem with expansion of international cooperation could substantially improve environmental management in both the Arctic and Antarctic.
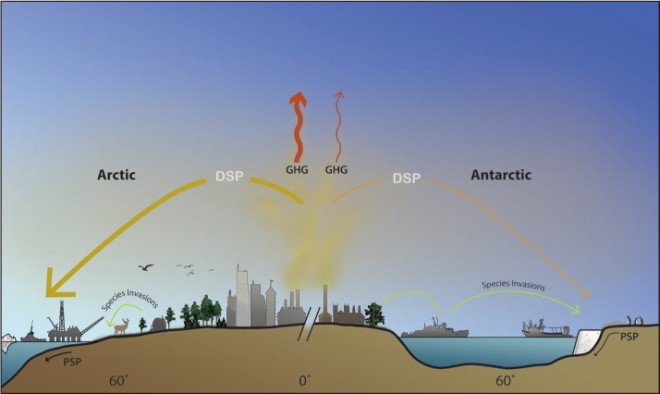
Figure 1. Shared threats to polar environments. Greenhouse gases (GHGs, red arrows) are the major causes of climate change, the principal threat to polar environments. Climate change interacts with other threats, including diffuse-source pollutants (DSPs) such as persistent organic pollutants and ozone-depleting chemicals that migrate from lower latitudes. It also raises the risk of more localized point-source pollutants (PSPs), as well as fisheries overexploitation (represented by fishing boats) and species invasions (green arrows).
READ MORE: Daniel Pauly and William Cheung