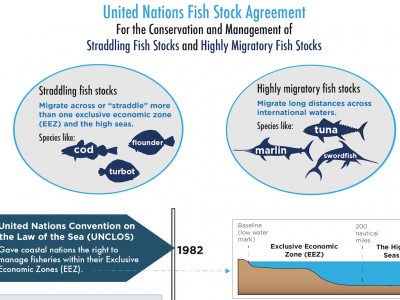
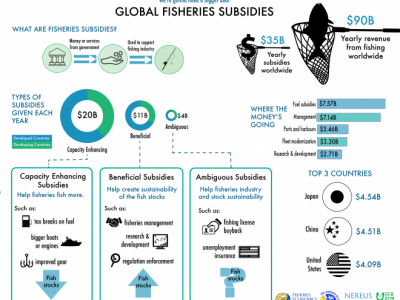
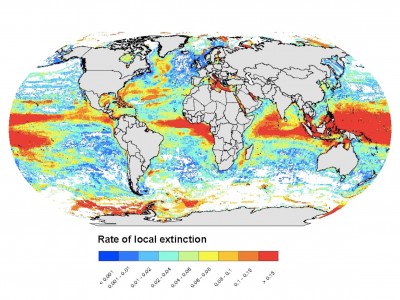
Illustrating the ocean: The process of depicting the complexity of marine ecosystems
By Jenn Paul Glaser, Nereus Program Consulting Artist
Our goal was to produce painterly digital collages that were conceptual in nature but grounded in state-of-the-art research. The culminating body depicted a total of about 30 species within at least 16 diverse marine ecosystems.